The design of commercial and institutional restrooms must now consider a range of factors in a integrated way, including not only water efficiency, durability, and accessibility, but also long-term use patterns. Designers are faced with considerations related to WaterSense, LEED v4/v4.1, ADA Accessibility, ASME, CALGreen, and code modifications.
This overview brings together these models and their application with regard to commercial toilets, urinals, and flush valves in high traffic situations.
Upgrading to WaterSense® certified commercial toilets (≤1.28 GPF) can reduce water consumption by up to 20% compared to federal standards, helping large office buildings save thousands of gallons annually. These efficiency improvements directly support LEED v4 Indoor Water Use Reduction credits, lowering operating costs while strengthening sustainability compliance and environmental performance metrics.
Framework of Voluntary and Regulatory Measures

Baseline codes and fixture standards
In most projects in the U.S., a model plumbing code like IPC or UPC begins with. These codes refer to ASME A112 series of performance specifications for commercial toilets and urinals in terms of structure, material, hydraulic performance, and dimensions. Some of the important ones are:
ASME A112.19.2 / CSA B45.1 – Ceramic plumbing fixtures
ASME A112.19.3 / CSA B45.4 – Stainless Steel Plumbing Fixtures
To eliminate discrepancies in performance in the bowl, geometry, trapway, wall-hung structural integrity, as well as compatibility with carriers and flush valves, it is important to identify the correct standard of ASME. In institutions where vandalism is a potential hazard, fixtures with a higher durability standard of ASME A112.19.3 in stainless
ADA and Accessibility Requirements
These are 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design, which regulate key elements such as center line location, grab bar arrangement, fixture height, fixture reach range, and operation of flush controls.
Useful reference pages:
ADA 2010 Standards for Accessible Design:
ADA 2010 Standards
U.S. Access Board, Chapter 6 Toilet Rooms:
U.S. Access Board – Chapter 6
Requirements of ADA affect plumbing fixture specifications, particularly when plumbing fixtures are considered. A WaterSense wall-hung bowl, for example, would not provide an ADA-compliant installation for the seat height without a corresponding carrier and floor finish depth. This early coordination overlaps with submittal and inspection conflicts.
WaterSense for Commercial Toilets and Urinals

Program overview
A key factor that contributes to this goal is that EPA WaterSense has set a common standard for efficient plumbing fixtures. Only third-party-validated products that meet this efficiency standard are allowed on the market.
WaterSense product specification index:
WaterSense Product Specification Index
Some commercially relevant categories are:
Flushmeter-valve
Tank-type Toile
Urinals, flushing devices
Certification further requires compliance with performance specifications of ASME. Maximum flush volume needs to comply with ASME.
“Flushometer”
WaterSense has established a flush volume of 1.28 gpf, no more than 20 percent below 1.6 gpf, a federal standard.
Overview and performance criteria:
Performance Criteria
Important engineering considerations
System design: The valve and bowl are certified in pair. Using different components without testing their combinations can result in sub-standard evacuation or wash performance of the bowl.
Hydraulics: The wash patterns, trapway configuration, and jet arrangement are required to comply with ASME testing requirements and consume low flush volume.
Wall-hung coordination: Preliminarily qualified combinations involve in-wall carriers. Unqualified combinations can void WaterSense certification.
Urinals
WaterSense-labeled urinals are usually 0.5 gpf or below, but before getting labeled, they must meet performance criteria.
Program details:
WaterSense Program Details
There are a number of states, including California, that have stricter volume maxima. The specifier must verify that selected urinals comply with WaterSense requirements as well as local code thresholds.
LEED and Water Use Reduction in Indoor Spaces

Water Efficiency
framework
Water modeling in LEED v4 and v4.1 is mandatory in new building projects. The key citations are as follows:
USGBC BD+C Guide: [USGBC BD+C Guide](<)
Guidance on LEED v4.1 Indoor Water Use Reduction:
LEED v4.1 Indoor Water Use Reduction
Important considerations
Requirement: Indirect Water Use for Internal Housekeeping – Minimum 20 percent reduction from EPAct 1992 Baseline
Credit: “Indoor Water Use Reduction – additional points for deeper reductions”
Conversion of Fixtures to LEED Calculation
An WaterSense-rated flush volume can help improve performance in design cases. Nonetheless, for LEED modeling, it remains dependent on:
Dual flush toilet weighted averages
Numbers of actual models in BIM scheduling
To avoid inconsistencies, plumbing schedules must include:
Volumini di scarico di riferimento
Design flush volumes.
Whether it has WaterSense certification
Flow data for all related valves and fittings
CALGreen and State Law
CALGreen mandatory measures
Therefore:
Minimum flush and flow rates are set in California by the CALGreen code for non-residential structures.
Important resources:
ICC CALGreen Nonresidential Mandatory Measures:
ICC CALGreen Measures
2022 CALGreen Water Requirements Summary:
2022 CALGreen Summary
CALGreen Plumbing Fixtures Requirements:
CALGreen Plumbing Fixtures
Volumes of CALGreen can be lower than those in federal EPAct. Reach codes are used in some jurisdictions for even lower volumes.
Integrate CALGreen, WaterSense, and LE
“Typical Workflow for California LEED Projects”
To set CALGreen minimum allowed flush volumes.
Use WaterSense labeled fixtures that support these principles.
To confirm the performance of LEED, national EPAct benchmarks are used
Since the baseline value for a LEED project is federal, a fixture that meets CALGreen requirements may not meet project water savings goals unless it has been modeled properly.
ASME Standards and Enduring Fixture Design
ASME Standards
These specifications, ASME A112.19.2 and A112.19.3, are still used as a basis for commercial fixture life and hydraulic performance
Wall-hung load testing
Trapway geometry
Water surface area and rim wash requirements
Just like in a conventional tank
Dimensional tolerances
Materials and glazing
High-traffic installations like airport terminal buildings and stadiums require fixture selections that are compliant with WaterSense flush volumes as well as ASME performance. The engineer should verify that:
The carrier systems comply with, and in many instances exceed, ASME load specifications
Mounting hardware is compatible with the fixture model
This ensures that all clearance specifications are met even with tile and floor thickness installation.
Incorporating Compliance Requirements in Project Specifications

Aggregating a coordinated fixture matrix
Each fixture
“A comprehensive plumbing specification and/or BIM fixture matrix should, but is not limited to, contain
Mounting type and rough-in information
Flush volume, valve type
ASME listing
WaterSense certification status
ADA application in every location
CALGreen Requirements or Regional Requirements
Comparison between LEED baseline values, design-case values
This will help avoid conflicts like improper seat height, conflict valve/bowl types, and differences between the LEED model and submittals for construction.
Controls, System Integration, and Metering
Electronic flush valves, in particular, bring in new considerations
Power supply and access in walls or prefabricated assemblies
Compatibility with Non-Potable Water Systems
Water use metering strategies for reporting of use, and strategies for maintaining LEED performance
Useful EPA resources:
WaterSense in Action: Toilets page
WaterSense in Action
Bathroom Water Conservation Guide: A Guide for
Bathroom Water Conservation Guide
Documentation and Submittal Strategy
Analysis A good submittal package should consist of: specifications with data sheets showing compliance with ASME, flush volume certified Confirmation of WaterSense labeling when applicable Water-efficient commercial toilets: Urinals: https ADA drawings and accessible layout documentation ADA Standards:
ADA Standards
Guidance from The Access Board:
Access Board Guidance
CALGreen tables and local amendments for projects in California
CALGreen Table
Local Amendments
Through early incorporation of documentation, tested pairings of fixtures, ADA needs, and LEED modeling, commercial restrooms can provide long-term performance, guaranteed accessibility, and quantifiable water savings throughout a building’s lifespan.
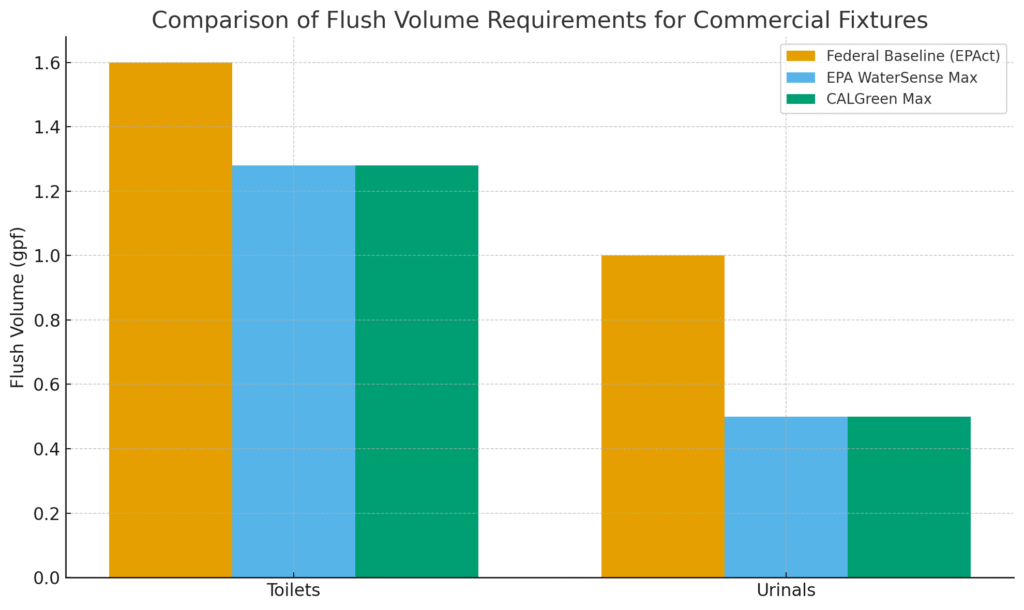
Flush Volume Comparison for Commercial Fixtures
| Fixture Type | Framework / Standard | Flush Volume (gpf) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toilets | Federal EPAct Baseline | 1.6 | National baseline used in LEED calculations |
| Toilets | EPA WaterSense Maximum | 1.28 | Requires certified valve + bowl system |
| Toilets | Typical CALGreen Maximum | 1.28 | Meets or exceeds state green code thresholds |
| Urinals | Federal EPAct Baseline | 1.0 | National baseline used in LEED calculations |
| Urinals | EPA WaterSense Maximum | 0.5 | High-efficiency urinals, often WaterSense labeled |
| Urinals | Typical CALGreen Maximum | 0.5 | Aligns with common CALGreen and local reach targets |

No responses yet